Demand sensing in 2023: A guide to getting started

Supply chain managers aim for precise future product demand predictions, but 100% accuracy and coverage is an overwhelming challenge. AI/ML technologies are improving demand forecasting for that short term insight, by leveraging recent-data within models such as PR news feeds.
Demand Sensing vs. Forecasting
Demand sensing predicts near-future demand using recent data, while forecasting relies on older data. Sensing captures short-term market trends.
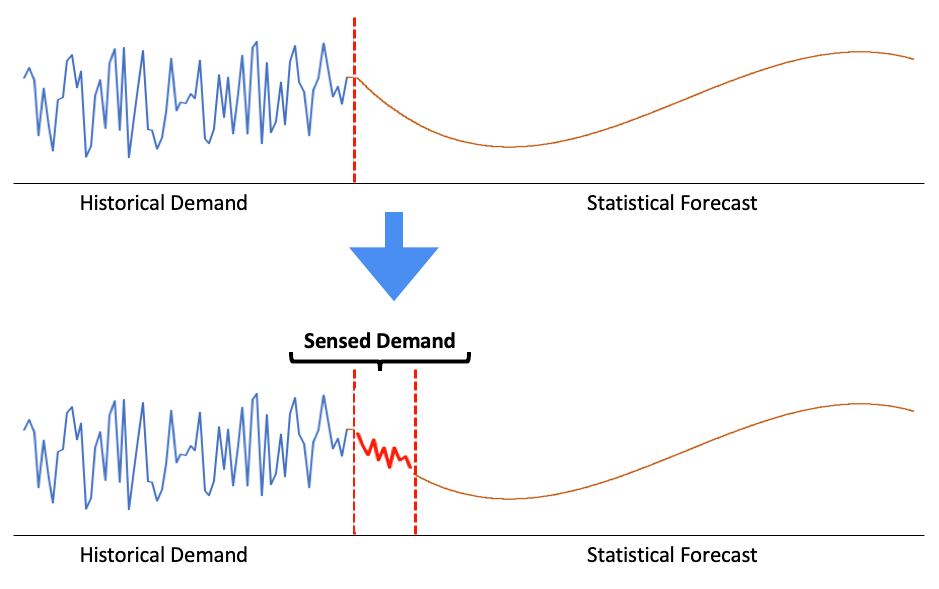
Unlocking the Benefits of Demand Sensing
Demand sensing can be a game-changer for supply chains, offering numerous advantages:
1. Enhanced Supply Chain Resilience
Short-term data derived from demand sensing equips supply chains to swiftly adapt to market volatility and unanticipated disruptions, such as the COVID-19 pandemic. This technological capability can significantly bolster the resilience and robustness of supply chains.
2. Optimized Inventory Management
Daily demand data provided by demand sensing enables the optimization of inventory levels. By reducing excessive stock levels, supply chains can become leaner without compromising their resilience. Ultimately, this leads to cost savings by minimizing excess production and handling expenses.
3. Improved Predictability
Demand sensing relies on a broad spectrum of signals, including real-world events such as order patterns, retail sales, promotions, and market dynamics. This multi-faceted approach empowers supply chains to identify trends earlier, aiding in more accurate decision-making.
Benefits of Demand Sensing
- Improved supply chain resilience.
- Enhanced inventory management.
- Better predictability using real-world signals.
Demand Sensing Best Practices
Start with Sell-In Data
Analyze granular historical data for accurate B2B demand forecasting. A straightforward approach to introduce demand sensing to your supply chain is to leverage granular historical data. This data can be analyzed to glean valuable insights for accurate B2B demand forecasting. Additionally, shipping history should be considered in conjunction with sell-in data, obtainable from any supply chain planning or ERP system.
Incorporate All Data Sources
Consider customer orders, POS data, and channel data for early trend prediction. Accurate demand sensing necessitates the inclusion of all pertinent data sources. These may encompass downstream sell-out data, including:
- Customer order data.
- Consolidated point-of-sale (POS) data, offering real-time insights into products sold, quantities, dates, times, regions, and more.
- Channel data.
The incorporation of such data aids in the early identification of emerging trends and serves as an early warning system against potential disruptions in the supply chain.
Include External Factors
Consider macroeconomic data, competitor insights, and weather for wider predictive horizons. A critical aspect that distinguishes demand sensing is its incorporation of numerous data points that are typically overlooked in conventional forecasting methodologies. Analysts should consider several external factors when implementing demand sensing, including:
- Macroeconomic indicators such as the country's GDP, stock market performance, employment data, and housing sales statistics, which directly impact consumer demand.
- Monitoring competitor data, such as promotional discounts or stock-outs. This information empowers supply chains to adjust their offerings strategically and gain a competitive edge.
- For businesses influenced by seasonal trends, the inclusion of weather data is vital. Weather data can help anticipate the short-term effects of weather changes on consumer demand, enabling adjustments to raw material procurement, production, and distribution plans.
By incorporating these external factors, demand sensing extends the horizon of its predictive capabilities, encompassing a broader range of potential events and trends.